Time Machine manages backups by creating snapshots that allow you to peer backward through time to select versions of documents, apps, folders, or other items that were later deleted or modified. Snapshots have a twofold purpose:
- They appear to represent all the files on the disk, allowing you to browse through the structure you know.
- They are compact, however, containing only the differences between the current state of your macOS startup volume and the last set of files stored. The first snapshot is, effectively, a full backup; the ones that follow, partial ones.
For some users, these snapshots can grow out of control. Readers write in regularly asking how to get rid of snapshots that fill their startup volume, making their system nearly unusable. I’ve provided answers in previous columns, such as “How to delete Time Machine snapshots on your Mac” and “How to fix your mysterious Mac storage problem.”
If you had a modern Mac, one running the APFS filesystem Apple began to introduce in macOS 10.12 Sierra, and were backing up to an APFS-formatted Time Machine volume, you had few tools at your disposal, as Apple relied on a different approach with its long-running HFS+ filesystem.
With macOS Monterey, Apple updated the Disk Utility app and its command-line counterpart to help manage APFS snapshots, whether created by Time Machine, Carbon Copy Cloner, or other software.
You can view snapshots by following these steps in Monterey with Disk Utility version 21:
- Launch Applications > Utilities > Disk Utility.
- Select your startup volume in the left-hand sidebar; with Catalina or later, select the volume group, labeled as “volumes.”
- Choose View > Show APFS Snapshots. (Note that Apple only shows this option in the system View menu, not the View menu labeled within the Disk Utility window!)
At the bottom of the volume view, you can see all the snapshots made for that volume. Double-click any snapshot, and it mounts in the Finder as a browsable volume. This can be much easier than using Time Machine to find a given set of older files.
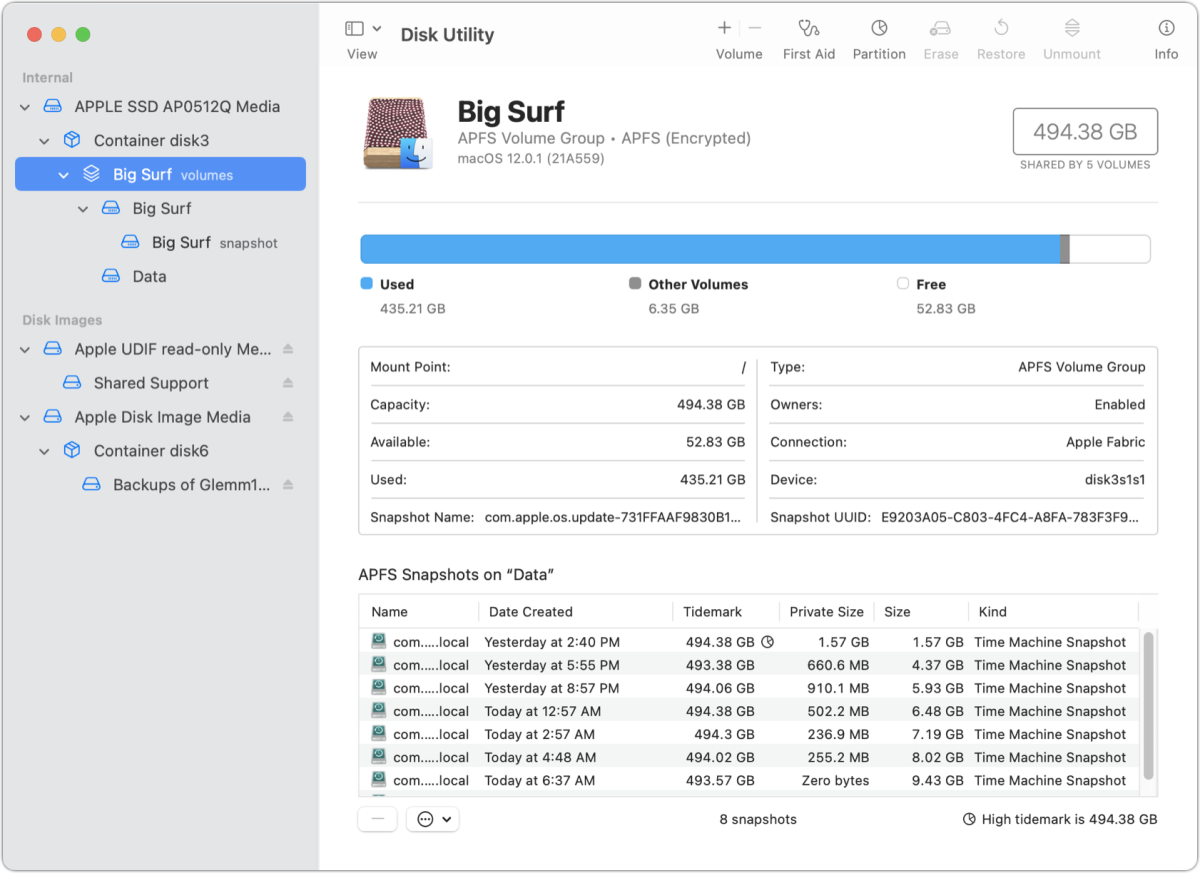
You can select any snapshot and click the – (minus) button beneath the list to delete it. Warning! This is irreversible.
To get a little more information in the list, click the … (More) button and choose Show Columns > Private Size. This reflects the actual space occupied on the drive by the snapshot. This is in contrast to the Tidemark, which tracks the smallest partition size that can be currently used to hold the active files and snapshots based on how data is structured in the snapshots. If you want to resize the container that holds the startup volume, it can’t be made smaller than the Tidemark value, which may explain errors you have seen if you’ve tried to resize such volumes and wondered where the missing storage was! Note in the figure above that the Used value for the volume group is 435.21 GB, but the Tidemark symbol (a partition icon) appears next to 494.38 GB, nearly 60 GB more.
(Tidemark is a technical term Apple only seems to define in the tooltip when you hover over the column title. It notes, obscurely, “The highest block referenced by a snapshot, which cannot be moved and limits shrinking its container partition.” More plainly, it’s a bit like Tetris or Jenga in that snapshots contain overlapping sets of changed files—you have to delete not just the latest or some snapshots to reduce the Tidemark, but ones that cascade to reduce the overlap required.)
Howard Oakley of Eclectic Light initially documented this solution and credits being tipped to it by someone else. Visit his article for more technical details, including how to use command-line options with tmutil.
Ask Mac 911
We’ve compiled a list of the questions we get asked most frequently, along with answers and links to columns: read our super FAQ to see if your question is covered. If not, we’re always looking for new problems to solve! Email yours to mac911@macworld.com, including screen captures as appropriate and whether you want your full name used. Not every question will be answered, we don’t reply to email, and we cannot provide direct troubleshooting advice.
